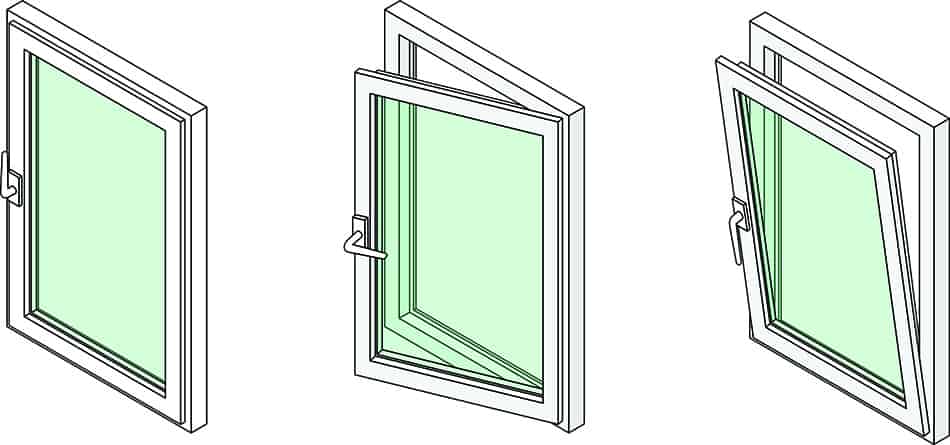
Replacing all or parts of your windows will not only improve your home’s curb appeal, but also makes your home more energy efficient. Windows come in all sizes, materials and designs, yet most of them are made of the same components. By understanding the different parts of a window and its frame, you can find the exact part you need.
In this article, We’ll start with the window frame then move on to the glass and other essential parts.
Window Frame
The window frame surrounds and supports the entire window. This essential part of a window is the outermost part and holds all the casements within one unit. This framework comprises the sill, jamb and head. Window frames are made of a variety of materials, including vinyl, steel, wood and aluminum. The frame is almost always attached to the building’s wall.
Sill
Also referred to as the stool, this main window frame part is the horizontal section that forms the bottom of the frame. Unlike doors, windows need a sill to protect their framework from damage or rot. If there is no sill, rain and snow would penetrate through the frame and cause damage. Aside from protecting the window, the sill can also serve as a decorative feature that looks attractive to the eye.
Head
The top horizontal section of the window frame is the head. It is parallel with the sill and since it’s located at the highest point of the window, it is referred to as the head.
Jamb
The side verticals of the window frame starting from the bottom to the top from left to right is called the jamb. This is an essential part of a window structure as it secures the panes or sashes.
Apron
This is a piece of decorative trim located beneath the sill or railing. The apron helps give the interior of the window a modern look.
Casement
A casement is surrounded by an upper and lower rail and stiles on each of its four sides. This part of the window frame may be fixed or opened from either the top, side or bottom.
Window Glass and Supporting Parts
The window glass is held together by a variety of different components. These are:
Pane
This is a single sheet of glass that makes up the pane.
Upper Panel
The upper panel part is either fixed or movable and holds the window pane.
Lower Panel
The lower part of a movable or fixed framework that holds the window pane.
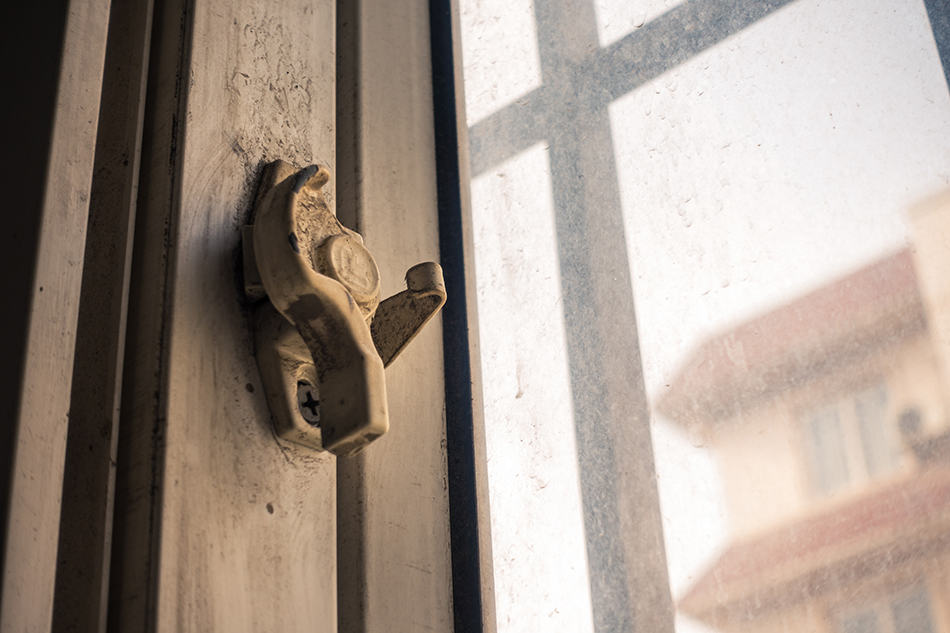
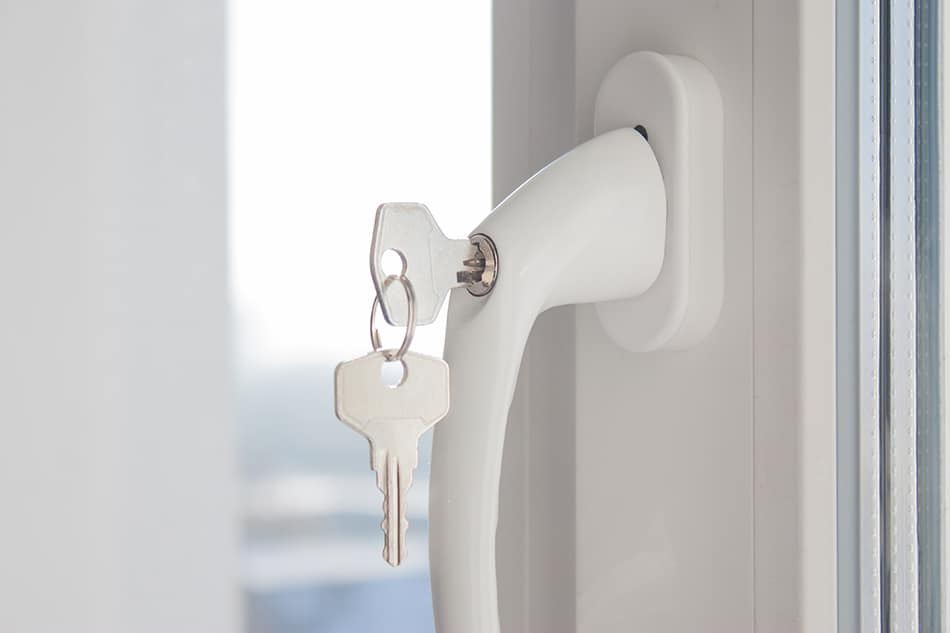
Sash Lock
This is the locking mechanism attached to a single or double-hung window.
Mullion
The vertical or horizontal structural component that supports two or more windows.
Muntins or Grilles
The material strips that divide the window glass to create a visual appearance of several glass panes.
Rails
On double-hung windows, there are three rails. The lower and upper rails comprise the horizontal section of a window pane. The middle rail, which is located in the center of the window, is where the lower part of the upper pane meets the lower part.
Types of Window Glass
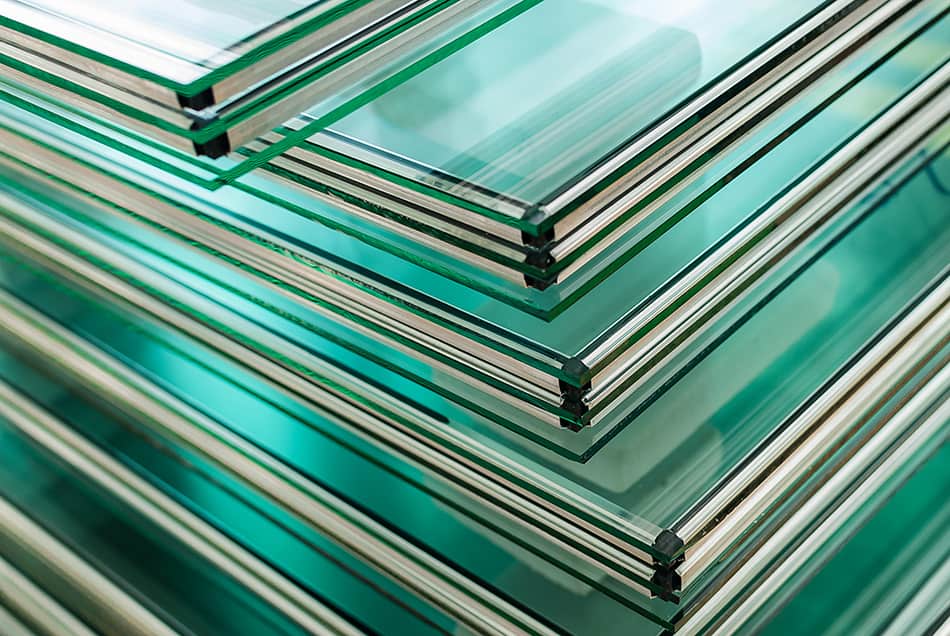
Tempered Glass
This is possibly the strongest type of glass you can find. It can maintain indoor temperature and won’t break easily.
Laminated Glass
This type of glass consists of a layer of poly-vinyl butyral to create a highly strong and durable glass sheet that’s shatter-proof.
Low E-glass
This is a low emission glass that’s specially film coated to reflect thermal radiation. In simpler words, it is designed to minimize the amount of UV light entering through the glass.
Other Supporting Parts of Window
Most windows aren’t complete without these supporting components:
Weep Hole
This is an escape route for condensation.
Weather-Proof Seal
All windows must have a weather-proof seal. This material can be made from vinyl, felt, rubber and metal.
Balance
This mechanical device is usually spring loaded and used in single-hung and double-hung windows to balance the weight of the pane during closing and opening.
Screen
This is a fine mesh made from aluminum or fiberglass to keep out insects.
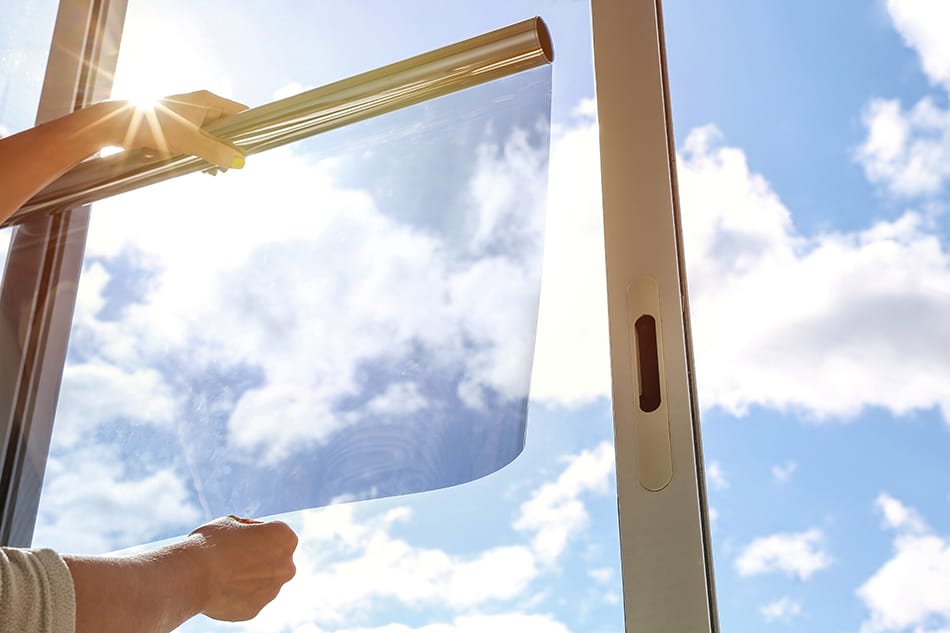
Window Film
This film reflects UV light and increases thermal efficiency.
Window Hardware
Depending on whether the window is designed in a modern or traditional way, the hardware may slightly differ. Here we’ll take a look at the most common hardware parts:
Locking Handle
This handle functions as a supporting feature to keep the window secure.
Stay
There are two functions served by window stays: the window will not be blown about by wind when it’s opened. When it’s closed, the stay position keeps the lower rail firmly in place so that the window doesn’t suddenly open.
Stopper Bolts
These stopper bolts prevent the window from opening when it is unlocked. When the window will be closed for a long time, this component can be unscrewed and attached right above the rail of the bottom pane.
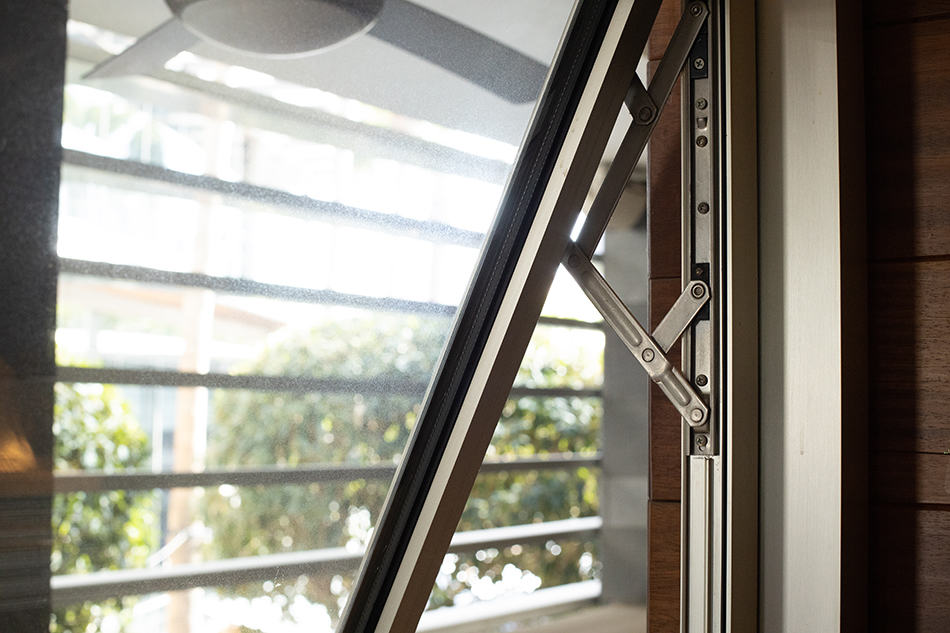
Hinges
The hinges of a window can be located anywhere depending on the window type. For example, casement windows feature hinges on the jambs, while on awning windows, the hinges are located at the frame’s head as the window is opened from the bottom. For hopper windows, however, the hinges are located on the sill as the window opens from the top.
Sash Window Lift
A lift is necessary for lifting the bottom half of the sash window. Although you can still use the muntins to push up or pull down the sash, some people prefer a lift instead.
Summary
Whether used as a decorative shelf to display your collectibles or for airing your rooms, windows are no doubt an important part of every home, so it makes sense to choose them carefully. They must be energy efficient, of high-quality materials and practical. The only way to save money in the long term is to understand all the different parts of a window in order to make a better purchase decision. We hope you found this article on window terminology useful. Feel free to share your comments below!